As part of its electric initiative, Volkswagen Sachsen GmbH is pursuing the goal of gradually producing several models of the so-called ID family. From November 2019, the vehicle plant in Zwickau will produce these models for Volkswagen and other Group brands such as Audi and Seat. The first assembly line has already been converted to production based on the Modular Electrification Kit (MEB). The different requirements of MEB production and the expansion to a multi-brand plant demand comprehensive measures regarding modernization and digitalization. The vision is to build the "leading plants in the application of Industry 4.0 technologies". This will enable the company to take the lead in the brownfield benchmark of the Volkswagen brand for the digitalization of large and small series production of electric vehicles and components.
Volkswagen Sachsen GmbH
> Strategy Consulting for Industrial IoT-Readiness
> Track & Trace
> Condition Monitoring in the ID. - Family
> Environmental Data Analysis in Vehicle Production

As a subsidiary of Volkswagen AG, Volkswagen Sachsen GmbH combines three Saxon production sites with a total of 11,000 employees: the vehicle production in Zwickau, the Gläserne Manufaktur (Transparent Factory ) in Dresden and the engine production in Chemnitz.
Strategy Consulting for IoT Readiness
Strategy Consulting for IoT Readiness
The Solution
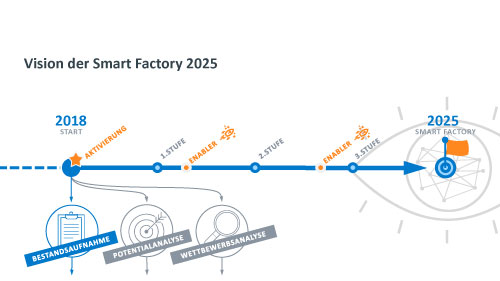
The "IoT Readiness" project assessed the current status of digitization in the individual trades of the automotive process chain, including logistics and quality assurance. The potential digitization topics are analyzed and evaluated together with the respective specialist departments and subsequently chronologically arranged in a roadmap. A process model was developed specifically for the requirements of digitization in the automotive industry. It is based on a holistic regulatory framework that considers people, technology and organization at the physical, infrastructural and virtual levels.
In order to meet the compact time frame, the process steps of maturity assessment, analysis of potential and competition were carried out in parallel. Following this pattern, solutions and application concepts in the fields of predictive maintenance, condition monitoring, edge computing, track & trace and cloud-based plant management were developed in collaboration with the Technical University of Dresden and the Dresden University of Applied Sciences. The aim of the project was to evaluate the status quo of the manufacturing system processes in terms of digitalization and IoT readiness by means of the Modular Transversal Kit (MQB). More than 50 meetings were held in nine areas, resulting in a total of 31 confirmed potentials.
The Benefits
The defined and developed topics for the IoT readiness strategy of Volkswagen Sachsen GmbH offer tremendous potential and corresponding cost savings of several million euros.
Examples include an intelligent sensor evaluation platform for carrying out root cause analyses. The aim is to improve the fault elimination process, and the use of IP cameras and artificial neural networks to increase the degree of automation in quality control.
The first projects have already been put out to tender and transferred to implementation projects.
Potentials of the digitization strategy:
- Reduction of manual processes
- Increased productivity and automation
- Reduction in the risk of errors and rework
- Consistent process transparency
- Optimized data management
- Proactive detection of production-critical conditions
The vehicle production in Zwickau consists of the usual production areas of body shop, paint shop and final vehicle assembly. The site also includes a pressing plant and competence centers for aluminum components and special vehicle construction. A high-performance pilot center is used for series preparation and support. The last combustion engine vehicle rolled off the production line on June 26, 2020. Since the founding of the site in 1990, more than 6 million vehicles have left the factory halls.
Track & Trace
Track & Trace
Initial Situation
With the introduction of the Modular Electrification Kit (MEB) and the implementation of new vehicle models at the Zwickau site, both the production and the pilot series volume of car bodies as well as the manual process efforts are increasing significantly.
In the course of this changeover, vehicle and body tracking will be transferred from the previous, manual and thus error-prone "clipboard" documentation on site to fast and digital tracking.
Project Objective
A vehicle and car body tracking system based on Bluetooth low energy technology (BLE) will be implemented in the project for a defined hall area of 2.17 ha with approx. 200 vehicles. This technology should make it possible to locate vehicles and car bodies in the above-mentioned hall areas and to visualize the current location via an application.
Solution
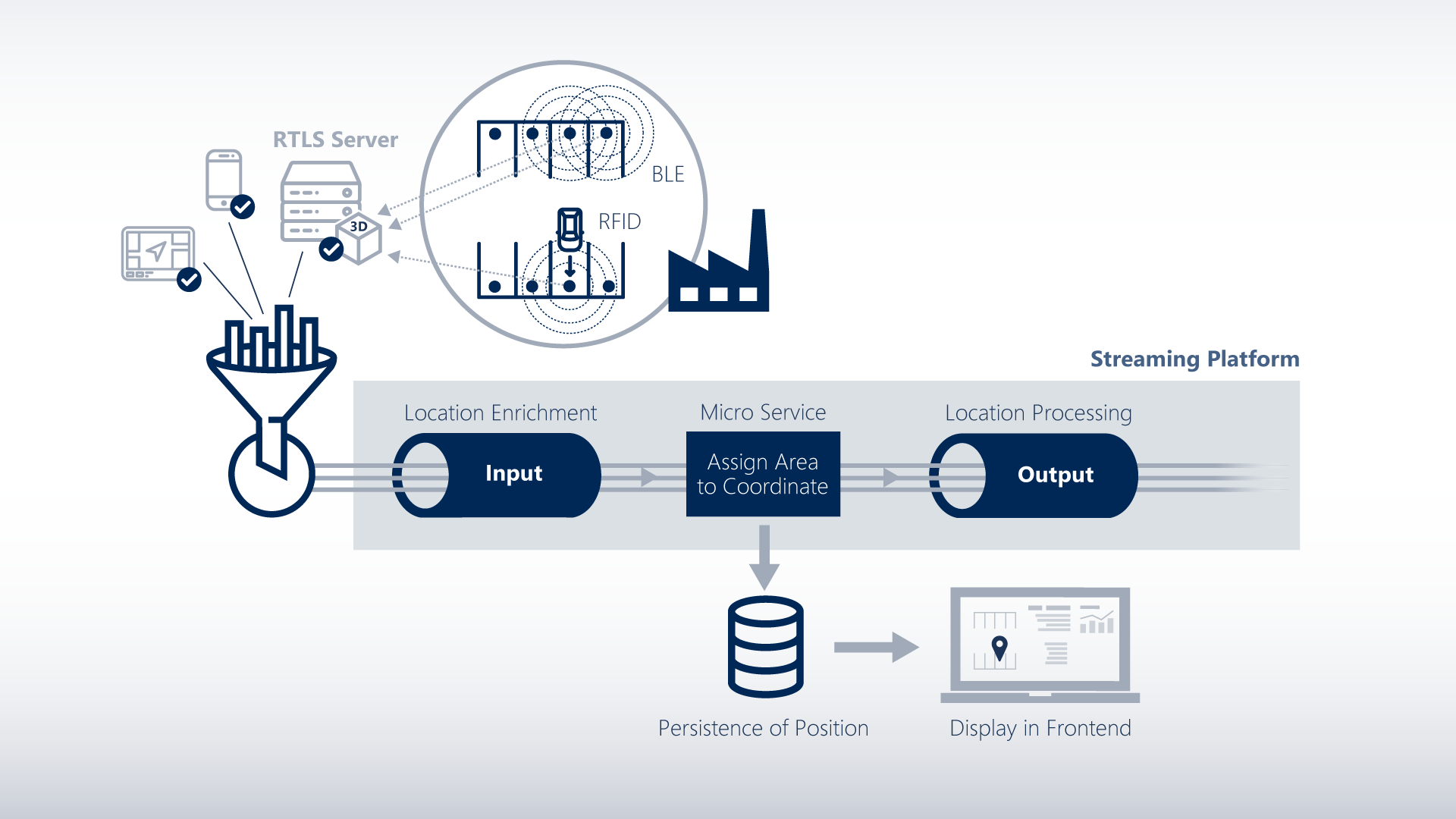
200 beacons with a transmission interval of 10 seconds were initially provided for the rollout of BLE-based localization. These beacons can be attached to the interior mirrors of the car bodies via a holding device. A further 90 BLE anchors were installed to receive the beacon signals and transmit them to a transfer point via UDP. The hardware is provided by the company ZIGPOS GmbH.
A streaming data platform based on a microservice architecture was selected as the central component for implementing the software applications. It is based on a Kubernetes environment that is built on a private cloud infrastructure and embeds the real-time location component ZIGPOS RTLS. The different stream applications, e.g. for pairing and unpairing the beacons and car bodies, as well as the Track&Trace responsive webapp are built on top of this. The vehicles and car bodies can now be visualized via the GUI with a grid accuracy of 10x10 meters.
A connection to the existing Plant Service Bus (PSB) based on the publish-subscribe pattern is implemented for the enrichment and further processing of the acquired data.
Benefit
The use of the Track&Trace solution enables fast and efficient tracking. This significantly reduces the high manual effort required to search for individual vehicles or car bodies.
Besides the connection of different consumer systems, the open platform approach also allows the integration of alternative tracking technologies such as UWB, RFID and LoRa. This results in many further areas of application and an extensive and diverse potential for use.
The vehicle production in Zwickau consists of the usual production areas of body shop, paint shop and final vehicle assembly. The site also includes a pressing plant and competence centers for aluminum components and special vehicle construction. A high-performance pilot center is used for series preparation and support. The last combustion engine vehicle rolled off the production line on June 26, 2020. Since the founding of the site in 1990, more than 6 million vehicles have left the factory halls.
Condition Monitoring in the ID. - Family
Condition Monitoring in der ID. Familie
The all-electric ID.3 and ID.4 are currently being produced in series in Zwickau. Vehicles from Audi, Cupra and Volkswagen will be added in the course of 2021. Six e-models for three Group brands will be built in Zwickau in the final expansion phase from mid-2021. The maximum capacity will be 330,000 vehicles per year. The site is thereby taking on a pioneering role in the transformation of Volkswagen's global production network.
Challenge
The completely redeveloped modular e-drive system (MEB) is being used for the first time in Zwickau. This places very high technical and organizational demands on the production plant in general and on each individual production step.
One example is the use of industrial adhesives in production. Due to the complex design, adhesive feeders are completely changed and then reprocessed. An evaluation of maintenance-relevant data helps to optimize maintenance intervals and avoid production downtimes.
Solution
Robotron reliably contributes to a more efficient use of industrial adhesives with robotron*IPEA. The solution ensures sustainable monitoring of the production of the ID. - models. The extensive evaluations of the software enable correlations of machine data with production information and thus permanent and comprehensive transparency on the condition of equipment in use. The data is sent from the machines via MQTT and initially feeds into a PSB and then into a distributed software architecture. So-called unsupervised learning is also applied in the project, in which the envelope methods learn independently from known inventory data. Maintenance staff consequently benefit from the integrated artificial intelligence and are proactively notified when an early maintenance is necessary before a problem occurs. In this way, the replacement of feeders becomes more efficient and downtimes can be better planned.
Benefits
The use of robotron*IPEA drives the change from cyclical to proactive maintenance. The integrated, transparent success reviews of the measures enable the assessment of decisions with regard to economic and ecological factors.
The benefits demonstrated in the pilot project can unfold their potential when the solution is rolled out to the entire bodywork. This is possible due to the solution's reusability for other lines, tool classes or entire production facilities.
Environmental Data Analysis in Vehicle Production
Acquisition, analysis and visualization of environmental data from vehicle production
The vehicles of the future will be more connected, more intelligent and, above all, more sustainable. In this transformation, the Gläserne Manufaktur Dresden not only represents a production site for electric vehicles, but also sees itself as a transparent showcase for the Volkswagen brand and an ambassador for the mobile future. Currently, 35 ID.3s roll off the production line in Dresden every day.
Challenge
Volkswagen Saxony (VWS) is intensively pursuing the goal of producing its fully electric vehicles in Zwickau and Dresden in a CO2-neutral manner. In 2019, the Transparent Factory Dresden (with the abbreviation in German being GMD) was the first Volkswagen brand location to produce carbon neutral vehicles when only considering the energy used by the assembly line. Reducing the carbon footprint of a company also plays an important role away from the manufacturing process. Another long-term goal is to control the building services of the Transparent Factory in a forward-looking, demand-oriented, and intelligent manner to further improve the carbon footprint of the production site.
As a starting point, more than 300 environmental sensors were installed in the GMD as part of a multi-stage pilot project to measure temperature, humidity, and air pressure continuously and comprehensively. The recorded environmental data was processed and visualised in dashboards to create data transparency enabling initial energy-related conclusions. The plan for the next stage includes using the measured data to make suggestions for intelligent operation of the building management system (BMS). In the future, the intelligent control system will be able to work more predictively and according to demand by using AI. This will make reaching the goal of total carbon neutrality more realistic.
Solution
The sensors for recording environmental data were installed at the relevant positions in the GMD. The recorded measured values are transmitted via ZigBee wireless technology to corresponding receivers, which forward them via MQTT to the Production Service Bus (PSB) of VWS. From there, the Splunk> Enterprise instance receives the environmental data for visualisation. Further environmental data from the machine controller responsible for the building services is collected with the help of the Robotron IoT Fieldgateway RoboGate. This is done to standardise it and to send it to an MQTT broker.
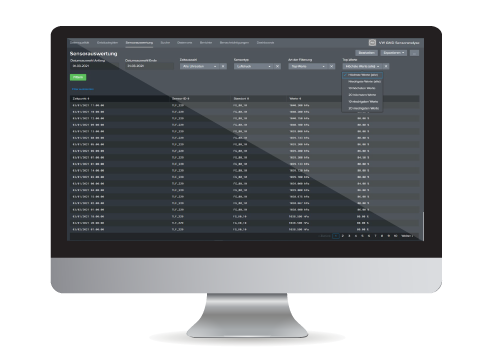
All data made available to the Splunk> instance is visualised in three customised dashboards.
The type of "outlier removal" (standard deviation or lower/upper limit) including parameters (factor of standard deviation) is defined in the data quality dashboard for each sensor type (temperature, air pressure, humidity, battery status). The dashboard also contains in a table the last data of the sensors including the last received messages as well as a table with the current settings of the respective sensor type.
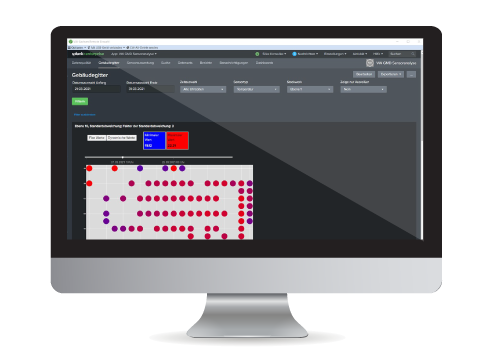
The building grid dashboard shows the core of data visualisation with Splunk>. The user has a comprehensive graphical representation of all relevant data in a "grid structure" of the building. The displayed data can be filtered with the help of various granularly adjustable criteria and set via numerous parameters. The user receives a compilation of the sensors positioned in it with their environmental data recorded in the selected time range in a coloured grid of the building. The dashboard offers additional interactive access to details of the sensor (coordinate, type) and the time history of the measurement data.
Benefit
The pilot project was successfully completed and provides evidence that the entire process from the collection of environmental data to its visualisation can be mapped in meaningful, easy-to-understand dashboards.
A comprehensive data collection and visualisation concept was created for the customer, which at the same time serves as a valuable basis for further and extensive evaluations. The integration of further data sources (e.g. weather data or forecasts, hours of sunshine, ...) is also possible to take external factors into account, e.g. the temperatures within the production line. The infrastructure created enables the data to be evaluated/analysed in addition to pure visualisation (e.g. to create forecasts, generate alerts, etc.). Combined with intelligent control of the building services, the Transparent Factory Dresden can finally take a big step towards proactive and climate-neutral production.